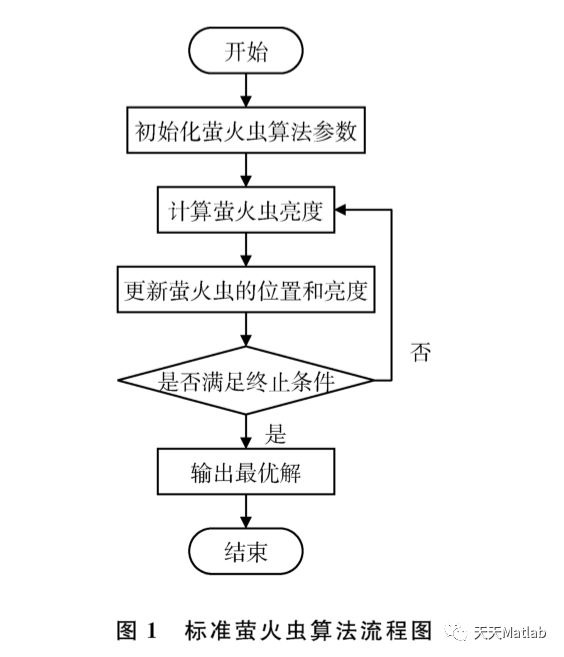
?1 簡介
一種基于螢火蟲算法的移動機器人路徑規(guī)劃方法.



2 部分代碼
clc;
clear;
close all;
%% Problem Definition
model=CreateModel();
model.n=3; % number of Handle Points
CostFunction=@(x) MyCost(x,model); % Cost Function
nVar=model.n; % Number of Decision Variables
VarSize=[1 nVar]; % Size of Decision Variables Matrix
VarMin.x=model.xmin; % Lower Bound of Variables
VarMax.x=model.xmax; % Upper Bound of Variables
VarMin.y=model.ymin; % Lower Bound of Variables
VarMax.y=model.ymax; % Upper Bound of Variables
%% GSO Parameters
MaxIt=50; % Maximum Number of Iterations
nPop=100; % Population Size (Swarm Size)
w=1; % Inertia Weight
wdamp=0.98; % Inertia Weight Damping Ratio
c1=1.5; % Personal Learning Coefficient
c2=1.5; % Global Learning Coefficient
%RANGE
range_init = 5.0;
range_boundary = 50.2;
%LUCIFERIN
luciferin_init = 25;
luciferin_decay = 0.4;
luciferin_enhancement = 0.6;
%Neighbors
k_neigh = 20;
beta = 0.5;
step_size = 5;
%% Initialization
% Create Empty Glowworm Structure
empty_glowworm.Position=[];
empty_glowworm.range=[];
empty_glowworm.luciferin=[];
empty_glowworm.Cost=[];
empty_glowworm.Sol=[];
empty_glowworm.neighbors=[];
empty_glowworm.Best.Position=[];
empty_glowworm.Best.Cost=[];
empty_glowworm.Best.Sol=[];
% Initialize Global Best
GlobalBest.Cost=inf;
% Create glowworms Matrix
glowworm=repmat(empty_glowworm,nPop,1);
% Initialization Loop
for i=1:nPop
% Initialize Position
if i > 1
glowworm(i).Position=CreateRandomSolution(model);
else
% Straight line from source to destination
xx = linspace(model.xs, model.xt, model.n+2);
yy = linspace(model.ys, model.yt, model.n+2);
glowworm(i).Position.x = xx(2:end-1);
glowworm(i).Position.y = yy(2:end-1);
end
% Initialize luciferin
glowworm(i).luciferin.x=repmat( luciferin_init , 1 , nVar);
glowworm(i).luciferin.y=repmat( luciferin_init , 1 , nVar);
%Initialize range
glowworm(i).range.x = repmat( range_init , 1 , nVar);
glowworm(i).range.y = repmat( range_init , 1 , nVar);
neighbors = [];
% Evaluation
[glowworm(i).Cost, glowworm(i).Sol]=CostFunction(glowworm(i).Position);
% Update Personal Best
glowworm(i).Best.Position=glowworm(i).Position;
glowworm(i).Best.Cost=glowworm(i).Cost;
glowworm(i).Best.Sol=glowworm(i).Sol;
% Update Global Best
if glowworm(i).Best.Cost<GlobalBest.Cost
GlobalBest=glowworm(i).Best;
end
end
% Array to Hold Best Cost Values at Each Iteration
BestCost=zeros(MaxIt,1);
for it=1:MaxIt
for i=1:nPop
end
% Update Best Cost Ever Found
BestCost(it)=GlobalBest.Cost;
% Show Iteration Information
if GlobalBest.Sol.IsFeasible
Flag=' *';
else
Flag=[', Violation = ' num2str(GlobalBest.Sol.Violation)];
end
disp(['Iteration ' num2str(it) ': Best Cost = ' num2str(BestCost(it)) Flag]);
% Plot Solution
figure(1);
pause(0.01);
end
img =gcf; %獲取當(dāng)前畫圖的句柄
print(img, '-dpng', '-r600', './img2.png') %即可得到對應(yīng)格式和期望dpi的圖像
%% Results
figure;
plot(BestCost,'LineWidth',2);
xlabel('Iteration');ylabel('Best Cost');grid on;
img =gcf; %獲取當(dāng)前畫圖的句柄
print(img, '-dpng', '-r600', './img.png') %即可得到對應(yīng)格式和期望dpi的圖像
3 仿真結(jié)果
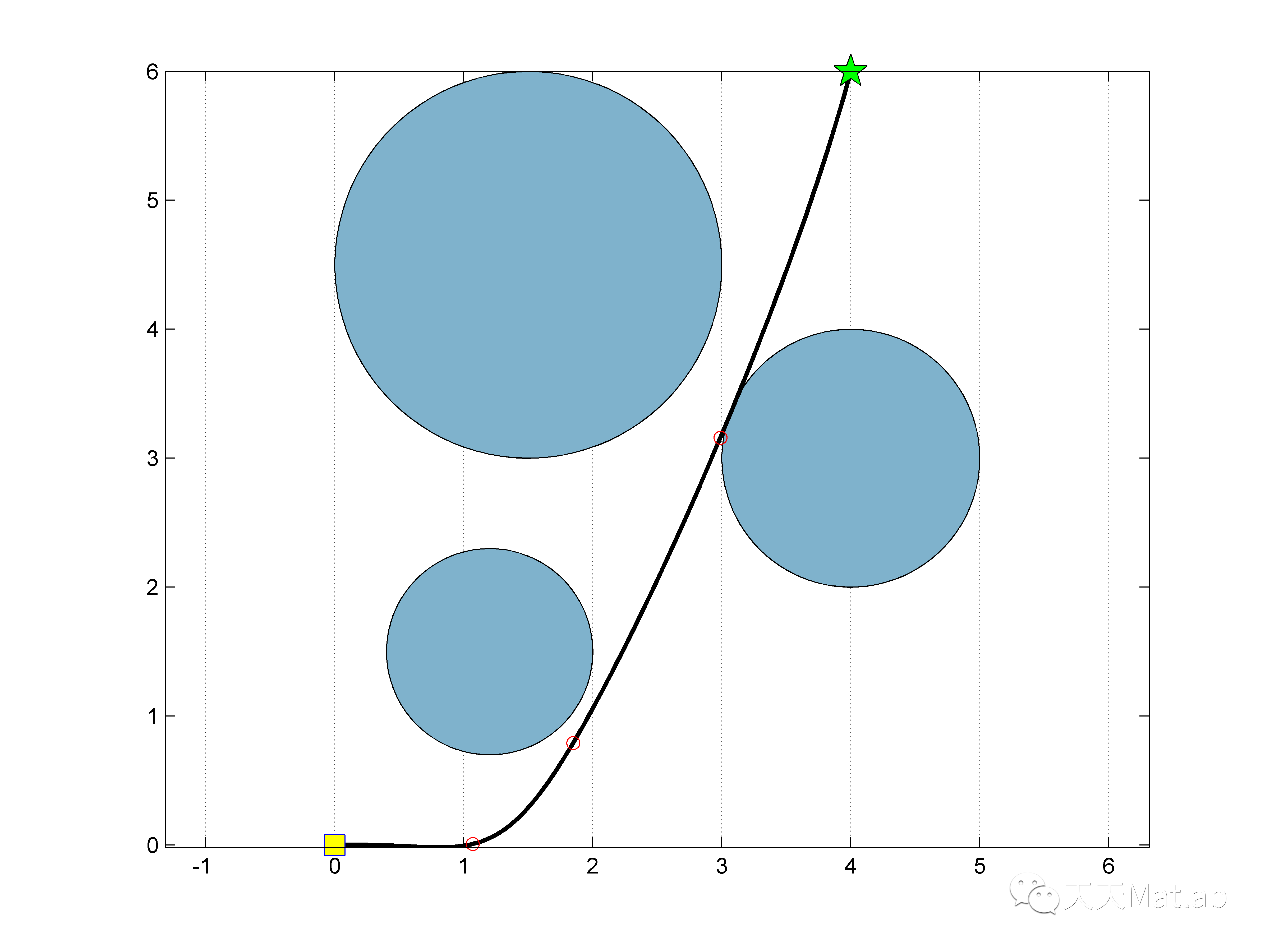
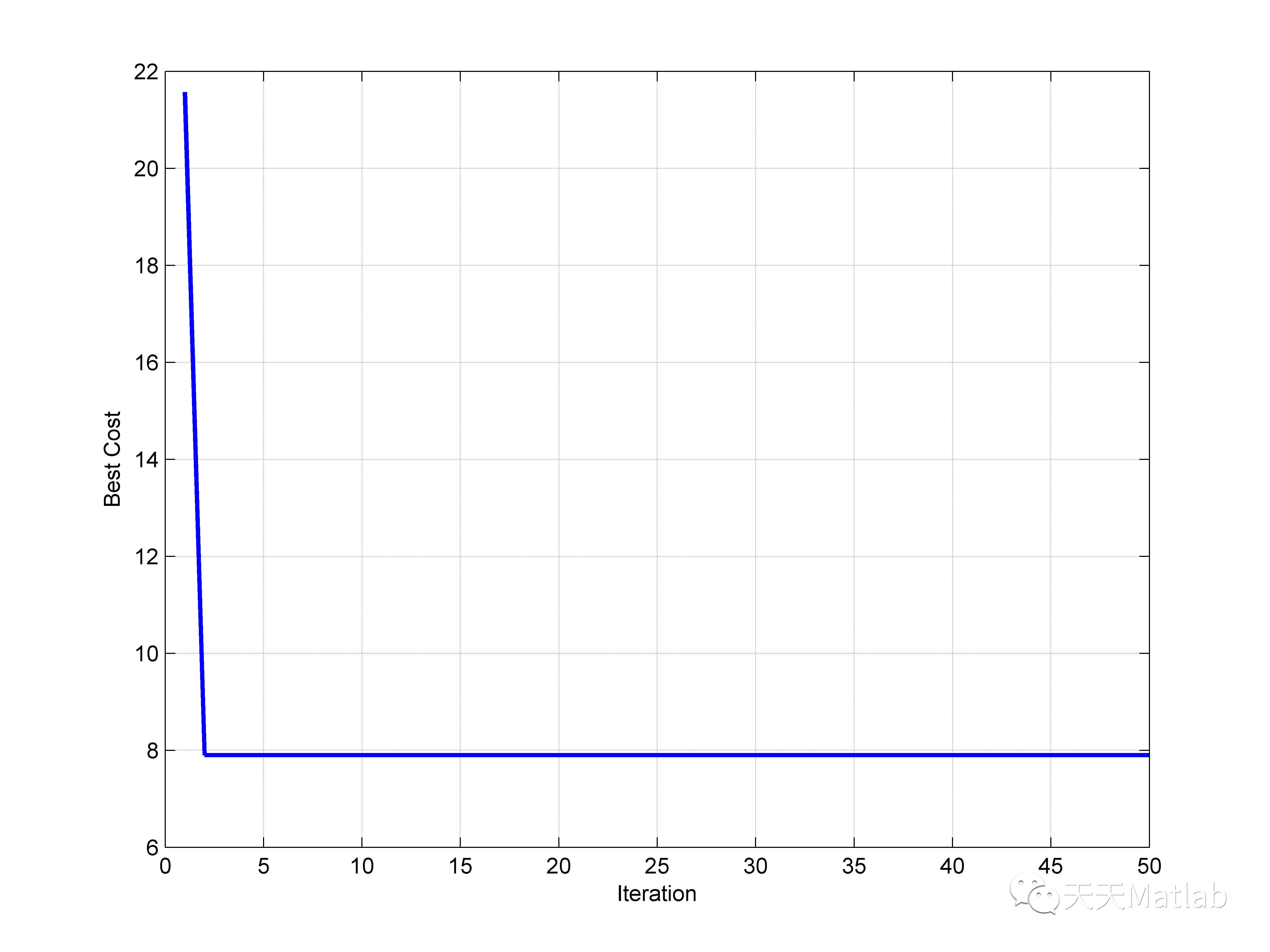
4 參考文獻
[1]李鳳玲, 陳珊, 范興江, & 劉源. (2019). 基于螢火蟲算法動態(tài)未知環(huán)境的路徑規(guī)劃. 自動化與儀表(6).

本文摘自 :https://blog.51cto.com/u

